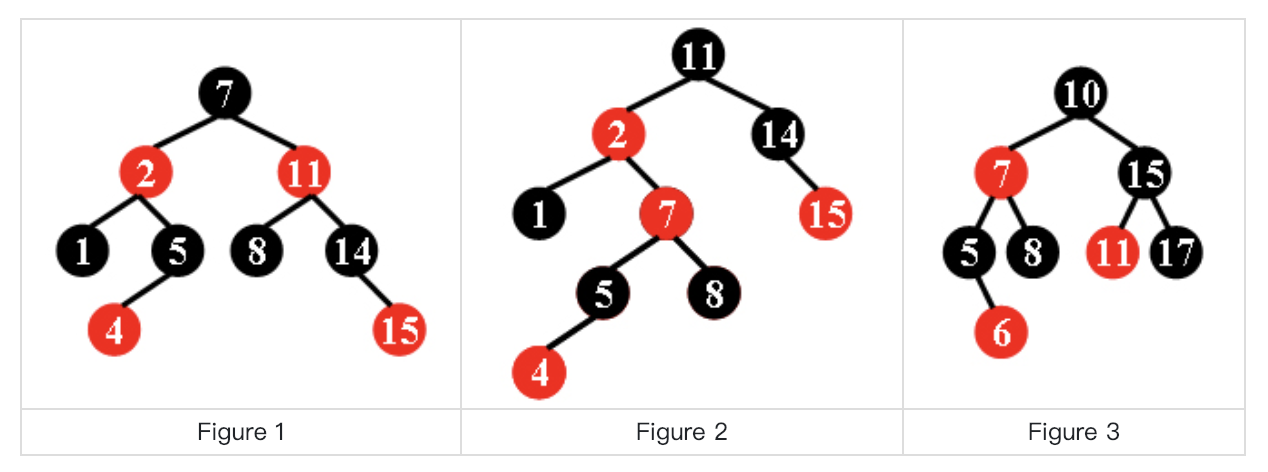
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
| #include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
int find(vector<int> tree, int s, int e) {
int i = s + 1;
while (i <= e && abs(tree[s]) > abs(tree[i])) i++;
return i;
}
bool solve4(vector<int> tree, int s, int e) {
if (s > e) return true;
int i = find(tree, s, e);
if (tree[s] < 0) {
if (s + 1 <= e && tree[s + 1] < 0) return false;
if (i <= e && tree[i] < 0) return false;
}
return solve4(tree, s + 1, i - 1) && solve4(tree, i, e);
}
int getH(vector<int> tree, int s, int e) {
if (s > e) return 1;
int i = find(tree, s, e);
int l = getH(tree, s + 1, i - 1);
int r = getH(tree, i, e);
return tree[s] > 0 ? max(l, r) + 1 : max(l, r);
}
bool solve5(vector<int> tree, int s, int e) {
if (s > e) return true;
int i = find(tree, s, e);
int l = getH(tree, s + 1, i - 1);
int r = getH(tree, i, e);
if (l != r) return false;
return solve5(tree, s + 1, i - 1) && solve5(tree, i, e);
}
bool isRBT(vector<int> tree, int n) {
if (tree[0] < 0) return false;
if (!solve4(tree, 0, n - 1)) return false;
return solve5(tree, 0, n - 1);
}
int main() {
int k = 0, n = 0;
scanf("%d", &k);
vector<int> tree;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
scanf("%d", &n);
tree.resize(n);
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
scanf("%d", &tree[j]);
}
if (isRBT(tree, n)) {
printf("Yes\n");
} else {
printf("No\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
|