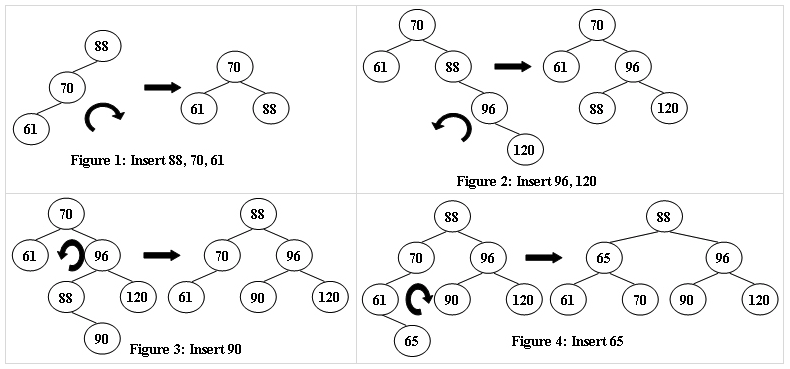
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
| #include <cstdio>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int inf = 65535;
map<string, int> s_to_i;
map<int, string> i_to_s;
bool visited[210];
int ans_len = inf, ans_kill = -1, defend[210], ans_path_cnt = 0, city_map[210][210];
deque<int> ans_p;
void dfs(int cur, int e, int n, int len, int kill, deque<int> p) {
if (cur == e) {
if (len < ans_len) {
ans_len = len;
ans_kill = kill;
ans_p = p;
ans_path_cnt = 1;
} else if (len == ans_len) {
ans_path_cnt++;
if (p.size() > ans_p.size()) {
ans_kill = kill;
ans_p = p;
} else if (p.size() == ans_p.size()) {
if (kill > ans_kill) {
ans_kill = kill;
ans_p = p;
}
}
}
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!visited[i] && city_map[cur][i] != inf) {
visited[i] = true;
p.push_back(i);
dfs(i, e, n, len + city_map[cur][i], kill + defend[i], p);
p.pop_back();
visited[i] = false;
}
}
}
void init(int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
visited[i] = false;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
city_map[i][j] = inf;
}
}
}
void printAns() {
printf("%s", i_to_s[0].c_str());
while (!ans_p.empty()) {
printf("->%s", i_to_s[ans_p.front()].c_str());
ans_p.pop_front();
}
printf("\\n%d %d %d\\n", ans_path_cnt, ans_len, ans_kill);
}
int main() {
int n = 0, k = 0, l = 0;
char own[4], enemy[4], town[4], city1[4], city2[4];
scanf("%d %d %s %s", &n, &k, own, enemy);
init(n);
s_to_i[own] = 0;
i_to_s[0] = own;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%s %d", town, &defend[i]);
s_to_i[town] = i;
i_to_s[i] = town;
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
scanf("%s %s %d", city1, city2, &l);
city_map[s_to_i[city1]][s_to_i[city2]] = city_map[s_to_i[city2]][s_to_i[city1]] = l;
}
deque<int> p;
visited[0] = true;
dfs(0, s_to_i[enemy], n, 0, 0, p);
printAns();
return 0;
}
|